snet-sdk-core
SingularityNET SDK core for JavaScript
Getting Started
This package provides the core functionality for interacting with the AI service daemon, handling connections, and managing payment strategies. It serves as the common foundation for both Node.js and Web JavaScript SDKs.
core– The main SDK functionality.nodeJS– Node.js-specific implementations.web– Web (browser) integrations.
Features
- Daemon Connection Management: Establish and maintain connections with the AI service daemon
- Payment Strategy Abstraction: Support for multiple payment methods with easy extensibility
- Request/Response Handling: Standardized communication with AI services
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Works in both Node.js and browser environments
- MetaMask Integration: Built-in support for Ethereum payments via MetaMask wallet
Installation
npm install snet-sdk-coreArchitecture
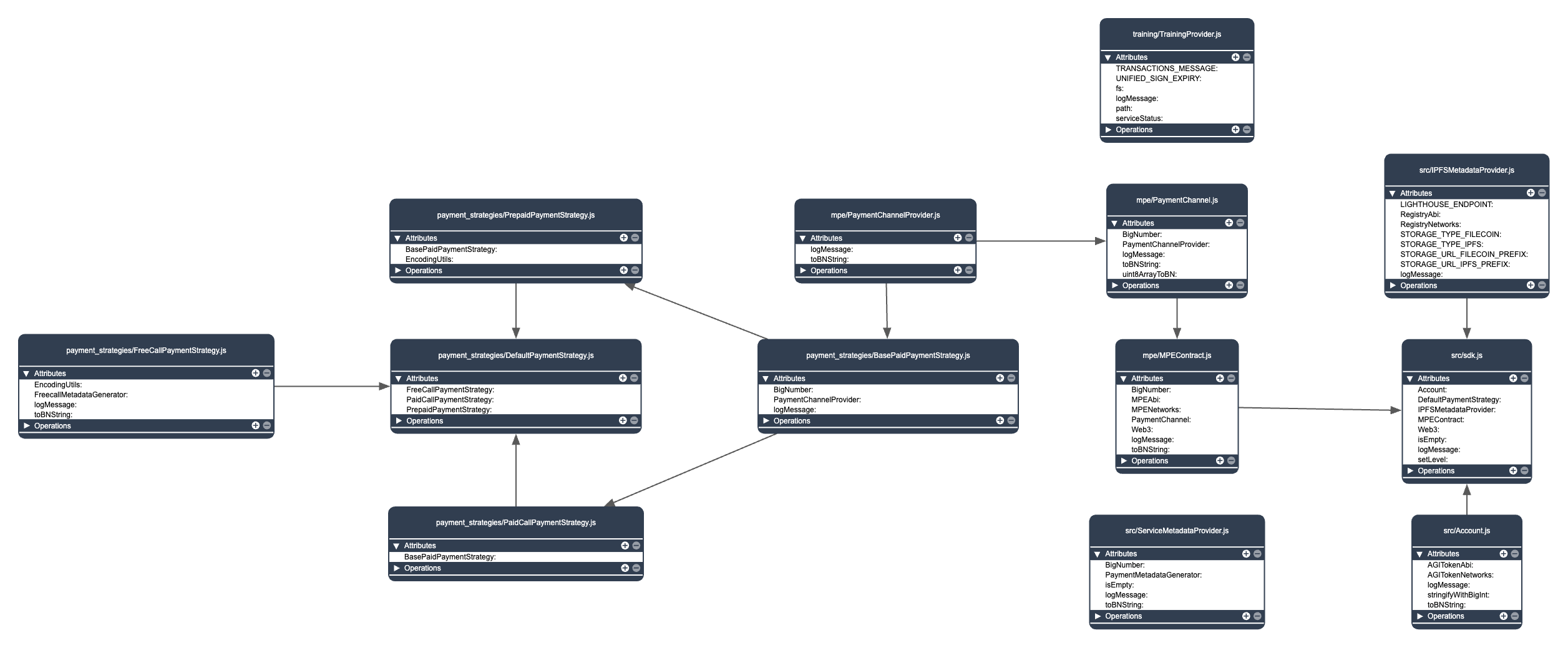
Usage
Prerequisites
Before using the Core JS SDK, ensure:
- Your wallet has sufficient ETH balance to cover transaction gas costs
- Your wallet has enough AGIX or FET tokens to cover service execution costs
Required Implementations
For a complete solution, you'll need to implement:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Service Client | Network communication handlers for your target environment |
| Payment Strategies | Web/Node-specific versions of Free, Paid, and Prepaid strategies |
| Wallet Adapter | Platform-specific wallet/account management |
| Stubs | Generate and use stubs from .proto depending on the type of platform |
Payment Strategies
Overview
The SDK provides three payment strategies:
Paid Pay-per-call model where each service call is individually charged
Prepaid Fund a prepaid balance that gets consumed with each service call. Ideal for:
- Concurrent service calls
- Batch processing
- High-frequency usage scenarios
Free Call Use available free call allowances (if applicable to your account).
Default (Recommended) The smart strategy that automatically:
- Uses free calls when available
- Falls back to paid strategy when free calls are exhausted
Since the Core JS SDK serves as the foundation for both Web and Node.js SDKs To implement a complete solution, you'll need to:
- Extend payment strategy classes
- Implement service clients
- Define method descriptors
Best Practices
Error Handling: Implement consistent error handling across all strategies a Testing: Verify each payment strategy works in your target environment
Type Safety: Use TypeScript interfaces for method descriptors
Development
Working on the Core Package
If you're making changes to the core package, you should test its compatibility with both the web and nodeJS packages. Here's how:
- Set Up the Workspace
Place all three packages (core, nodeJS, and web) in the same parent folder.
Example structure:
/workspace/
├── snet-sdk-core/
├── snet-sdk-nodejs/
└── snet-sdk-web/- Build the Core Package
Navigate to the core package and run:
cd snet-sdk-core
npm run buildThis generates the compiled output in snet-sdk-core/dist.
- Link the Local Core Package
In the nodeJS and web packages, replace the snet-sdk-core dependency with a local file reference.
Update their respective package.json files to:
"snet-sdk-core": "file:../snet-sdk-core/dist"Then, reinstall dependencies in each package:
npm installNow, changes in the core package will reflect in the dependent packages during development and you can check all functionality using examples of web and nodeJS SDKs.
Handling Signature / Binary
The grpc API metadata is a map of key, value pair to store the headers.
The value can be either String or Buffer.
All binary headers should have -bin suffix in their names. Vice versa.
A String header's name must not end with this.
NodeSDK and WebSDK use grpc and @improbable-eng/grpc-web respectively to make grpc API calls.
LICENSE file for details.